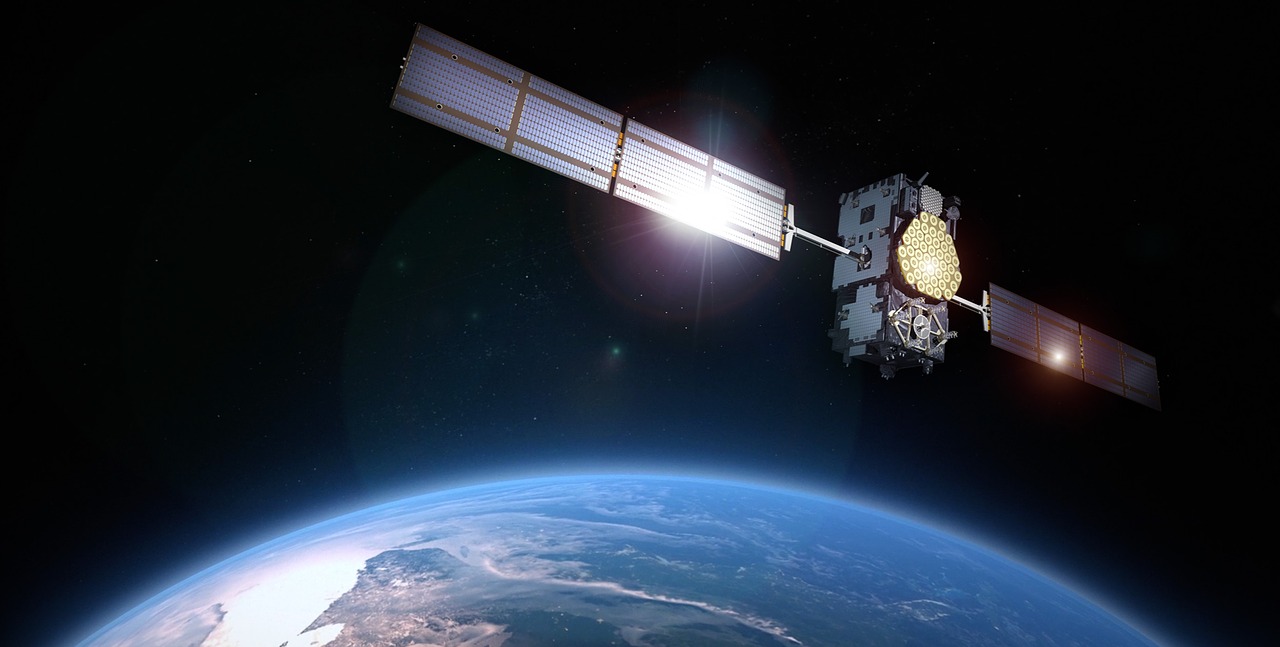
Communications satellites orbiting around the Earth are designed to receive telephone, radio, and television signals. A station on Earth sends signals to a satellite, which then retransmits the signals to a receiver on the ground.
Communication satellites can provide telecommunication across long distances and to remote locations, such as ships in the ocean. Before the bandwidth capacity of cable technology was improved with fiber optics, satellites provided a more reasonable method of telecommunication.
What is a satellite?
A satellite is any object that revolves around another bigger object. Satellites can be classified in two categories: artificial and natural. A natural satellite is an object that occurs naturally, such as a meteor or moon, orbiting a larger object in space, such as the Earth or another planet. The Earth is actually a satellite of the sun. A manmade communication satellite is an example of an artificial satellite.
More than half of the active satellites in orbit are used for communication purposes. Estimates show that there are about 2,000 active communication satellites orbiting around Earth. When a satellite is no longer active, it is regarded as space debris.
All of the Earth’s communication satellites are located about 22,000 miles above the equator. The altitude means that the satellite orbits in about the same amount of time that the Earth makes a 360-degree turn. Thus, from the ground, it appears that the satellite is stationary and always positioned above the same part of Earth.
Robotics made satellites possible
All of the currently active communications satellites are operated robotically, meaning there is no need for an astronaut on board to manage them.
The ability of communications satellites to operate without a crew on board was a major factor in their development, as it costs a lot to support a human in space. By operating robotically, these satellites no longer needed to account for human space or support, which made them more compact and affordable. In fact, some of the communications satellites currently floating out in space are as small as a shoebox.
Launching satellites into space
Artificial satellites are launched into a specific orbit via rockets. The satellite is attached to a rocket, which is launched directly upward into space, driving the satellite through the thick part of the atmosphere.
The rocket carries technology that allows it to position the satellite in the proper orbit path. Once it is properly positioned, the rocket releases smaller rockets toward the east so the satellite receives a little push to the west, the direction that the Earth is orbiting.
Flight paths are created for satellites so that they don’t crash into other satellites, which has been known to happen. For example, in 2009, a pair of American and Russian communications satellites ran into one another.
Drawbacks of communications satellites
Building satellites and sending them into space is expensive, which is a drawback for satellite telecommunication. Additionally, satellites can cause major delays in sending and receiving signals, which can present a challenge in terms of the average phone call.

Despite these drawbacks, there are still some forms of telecommunications for which satellites are very useful, particularly in connecting with remote locations such as airplanes or ships where it isn’t possible to lay a cable.
Evolution of communications satellites
In 1945, satellite communication was first suggested as a concept. What history recognizes as the first communications satellites was launched in 1958. President Dwight Eisenhower used the original satellite to relay a holiday message to the globe.
By the early ‘60s, two additional and successful satellites had been launched: Telstar and Relay. Early models required massive antennas on the ground to send and receive signals on Earth. The communication satellites were only used for transmitting television signals and making long-distance phone calls. The technology had improved enough by the ‘90s that more than 60 percent of non-local phone calls utilized satellite communication.
Brazil launches new satellites
Many countries are still actively launching satellites into orbit to improve their connectivity. Brazil has initiated a program to provide better Internet and broadband services for the country’s civilians, military, and space industry.
As part of this program, satellite launch company Arianespace has sent multiple telecommunication satellites into space on behalf of Brazilian telecommunications company Embratel.
Satellites and the future of telecom
The delay in signal reception and transmission—called latency—means that satellite communications aren’t useful for several modern forms of communication such as video conferences and interactive games. However, many experts believe that satellites have excellent potential for delivering television and music to Internet users. It is possible that the orbit of future satellites will be closer to Earth, which will mean a shorter distance for signals to travel and thus less latency.
Satellite communication will always be a better option in places that are not connected by underground cables. Additionally, satellites provide a secure backup for communication when cables are damaged or threatened by a natural disaster.
Communication satellites as we know them—devices floating around in space—might change. A US-based company is experimenting with mounting broadband transceivers onto commercial airliners in order to create an Airborne Wireless Network (AWN). This would negate the need for communications satellites in space and replace that technology with a network created by planes.

